Bonding study: Fostek automotive and industrial EPDM foams
Determining the correct adhesive when bonding to foam and other materials may be challenging, especially when seeking to provide your customer an accurate quote quickly and accurately. To help you with the adhesive selection, and the technical requirements your customer may require, Avery Dennison Performance Tapes has developed a series of adhesive bonding studies. These studies highlight the performance of our Core Series™ Portfolio products when combined with foams and other materials from industry leading manufacturers.
Bonding to Fostek automotive and industrial EPDM foams
Founded in 2004, Fostek Corporation continues to develop and manufacture high-quality engineered foams approved and specified by OEMs, Tier 1s, as well as other manufacturers worldwide. Fostek's IATF 16949 certified process benefits design engineer sealing. EPDM is well known to be a viable polymer option foam versus cast PVC in many performance comparisons.
Fostek also developed a proprietary technology for its diverse family of vinyl/nitrile/neoprene blend foams. These foams deliver outstanding physical properties, mechanical performance, and compatibility with wide varieties of pressure-sensitive adhesives. Fostek’s vinyl/nitrile/neoprene blends are generally known for their durability and resistance to oil. Fostek foams possess a high process capability allowing its products to meet or exceed automotive and non-automotive specifications.
Fostek’s facilities and processes are IATF 16949:2018 certified to ensure the highest quality products for automotive related products as well as the rest of our family of non-automotive products.
Fostek automotive and industrial EPDM foams and Avery Dennison adhesive sample preparation
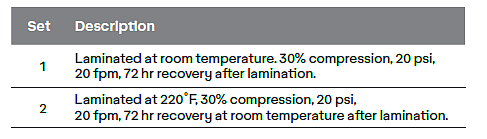
Avery Dennison adhesive products were backed with a 2 mil PET film and trimmed to a one-inch width. Two sample sets were laminated to Fostek Industrial EPDM Foams.
Fostek automotive and industrial EPDM foams and Avery Dennison adhesive sample testing
Foam bonding is affected by the foam's base polymer, thickness, and cell type. Adhesion to foam is impacted by factors such as: adhesive mass, pressure, compression, lamination speed and temperature. All samples were tested at 180° Peel Adhesion at 12 in/min. It was determined by this study that heat lamination is beneficial (220˚F).
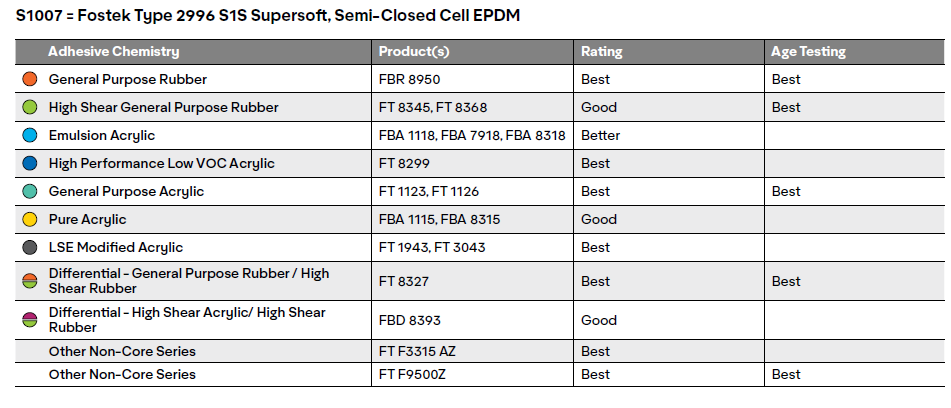
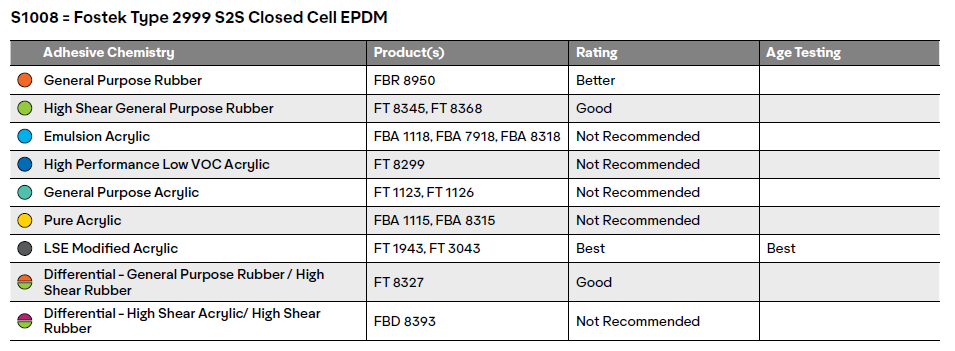
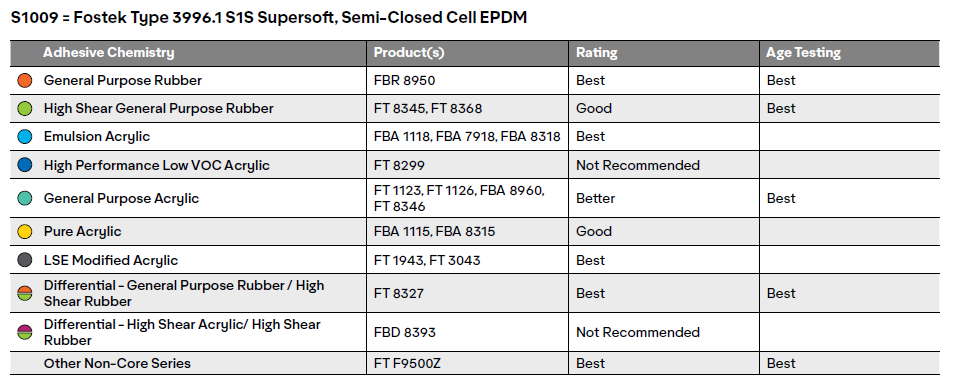
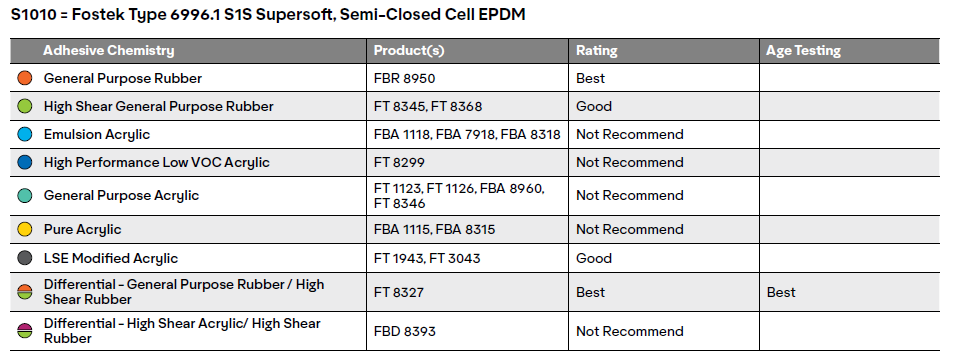
Good = Likely to achieve foam tear with heated lamination.
Better = May achieve foam tear without heat lamination.
Best = Likely to achieve foam tear at room temperature
Heat Age = For the accelerated age testing (ASTM D3611), the foam was laminated at room temperature then placed in a chamber and subjected to 66C (150F) and 80% RH for 96 hours. This simulates roughly two years of aging. The samples were then tested at 180 degree peels at 12 inches per minute. Products that achieved foam tear after repeating the accelerated age testing received the Best rating.

